Table of Content
Whether you’re in the planning phase or have already implemented NTFS permissions, following some best practices ensure smooth administration and aid in resolving access issues quickly. Security is set for that single user either manually (if I've cocked up the process) or normally by AD when creating the user and setting their home folder. Currently we are working to secure our internal LAN and due to this we are planning to stop mobile devices to connect on corporate network. I'm trying to help clean up and potentially automate the creation of a folder for a specific subset of users. Hopefully I can make sense of the current structure now and what we'd like to accomplish.
User groups should only be used to group together staff members that are part of the same organizational unit . You want to make sure the folder that HOLDS the user folders, is set so everyone can read for this folder only. Then the user folders within said folder are where you're going to have to assign the specific permissions. So you'd want to set it so john_smith has permission over the john_smith user folder . Our folders/files already exist on a server and I am moving to a new server and want to set permissions correctly. Great responses and the server software makes it fairly easy to get this done.
How to Set NTFS Permissions Correctly
She is also a book lover, cineaste and passionate collector of curiosities. I've managed something like this before but its been quite some time. I'd like to avoid having the helpdesk perform so many manual steps that inevitably go afoul.

I have not been able to find a way to have a user able to access just their folder in the Home Folders, without being able to access everyones. For example, if a user needs to read information in a folder, and should never delete or create files, assign only the “Read” permission. These structures become especially confusing when permission groups are nested within themselves or within other permission groups by mistake.
Best Practices for Using Permissions
When pulling new files from a remote repository’s URL into a remote-cache, the user performing this request must have deploy/cache permission. Do not set explicit NTFS permissions on deep levels in the directory. Limit the number of levels to 2-3 in order to keep things clear and simple. The number of permission groups and list groups needed to manage explicit permissions on deeper levels quickly grows out of control.

This process should be avoided because it makes it more difficult to read NTFS permissions and, as a result, permission structures become confusing and chaotic. Users who have Read and Execute access to a specific folder must also have the List Folder Contents permission for any higher-up folders in order to navigate to their target. The List Folder Contents permission should be assigned via group membership. By using nested groups, you can ensure that each user automatically receives the NTFS permissions for browsing when they are given the relevant permissions to the subordinate folder.
Best practice for home folders?
This can help you when defining a given Permission Target, as your projects will contain your repository list. This not only serves as your guide but also as something you can share with other admins in your group to ensure everyone is on the same page. By using tools such as FolderSecurityViewer or Effective Permission tool, you can examine and see the permissions each user has and act upon them accordingly. Doing so prevents unauthorized access to critical data, making your environment more secure. Here are seven practices we find effective in managing NTFS permissions. We actually have the user's Documents folder redirected via group policy as well to the server.

I would recommend not having users "Home" folders nested inside of your "Shared" folder. However if you do make sure that you block inheritance on your Home folder so it does not automatically inherit permissions on the Shared folder. “Read & Execute” permits only viewing, accessing, and executing the file. This way, it’ll prevent application files from being accidentally deleted or damaged by users or viruses.
Howto block personal devices on corporate network
You'd also need to consider what happens when people's managers change, so maybe create a function that could create folders if they don't exist, or simply fix up permissions if they do. We have a similar setup as Dave Murray for the users home drive. I do not share the user folder and only the user, system, and administrators have access. When we have users that quit, retire, or are fired I zip up the folder and archive it to another location. If someone such as the manager asks for access to the files I provide them a copy of the zip file.
Furthermore, consolidating folders with the same security requirements will assist in managing their access rights. In accordance with the Principle of Least Privilege, each user should only be given the minimum level of access required to do their job. Eliminating unnecessary permissions prevents them from being exploited in the case of a cyberattack or insider threat, thus making your Active Directory and file server more secure.
When you assign permissions for working with application folders, assign the “Read & Execute” permission to the Users group and Administrators group. It’s a good practice to give “everyone” full control privileges on the Share Permission and then define specific permissions on the NTFS level—just as Microsoft has recommended it. Today, we are going to take a look atfive common mistakesmade when setting NTFS permissions. To help you avoid errors like these, we will also walk you through thebest practices for NTFS permission management. I got it working where newly created folders generated from AD when creating a new user, but there is a bunch of already existing folders that would need to to work the same way.
This leaves me with the exact image of the folder when the person left. In our agency each user has a home folder , then we have a separate Shared Folder that has limited access on an as needed basis and a separate folder for profile folders. All folders have security set at the parent folder level and permissions are set with security groups, not individuals, except for their home folder and profile folders. Let access-based enumeration help keep the home folder secure. When creating user folders under Home, remove all inherited permissions except System and Administrators, then add the user with Modify permissions.
This might save time in the moment, but ends up creating a lot more work in the long run. This article has been written to help you to setup correct permissions for the home folder in active directory domain services in Windows Server 2012 R2. Individual roles should be defined within the context of the groups that you define. Your groups can be created manually or, depending on the authentication method in use, imported into Artifactory.
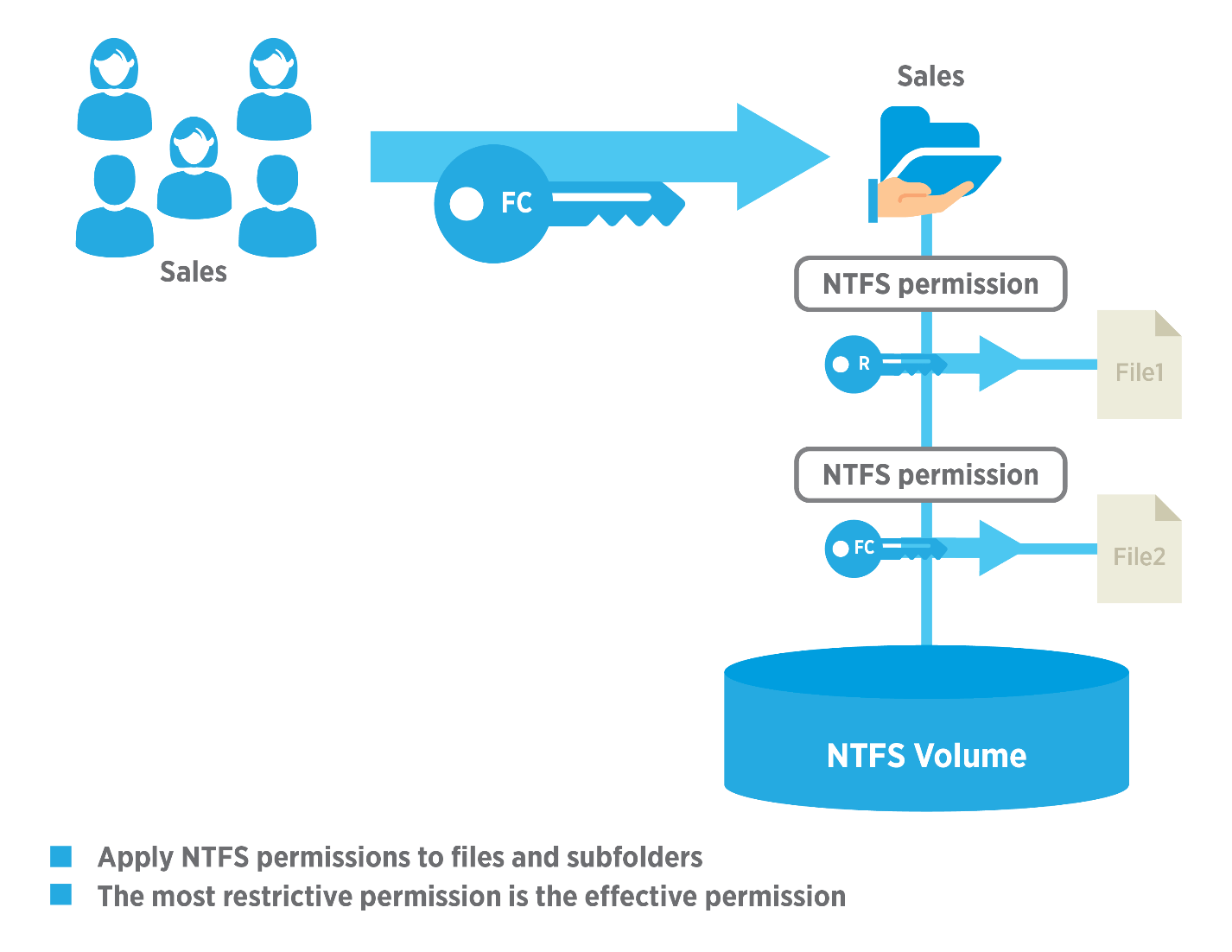
While any administrator knows how toset or change NTFS permission levels, the tricky part is how to manage them consistently and efficiently forhundreds or thousands of different users. By making permission groups members of the list groups for directories above their folder, users automatically receive the necessary permissions when they are given access to a resource. It is, however, very important to restrict inheritance to ensure the ability to view folder contents only applies to the folder in question, not other folders within the same directory. Yes, it takes time and effort to create, name and manage hundreds of different groups. But it’s still a lot easier than trying to balance thousands of individual permissions. When file access needs to be adjusted later on, would you rather make one change to the relevant permission group or change the settings for dozens of individual users?
NTFS permissions allow you to grant directory access to individual users and groups. In contrast to share permissions, where the choice of permission levels is limited to Read, Change or Full Control, NTFS permissions offer much more granular control. NTFS permissions are used tocontrol accessto files and folders in Windows environments and are particularly relevant for directories that aresharedover a network.

Among other benefits, this will help save network share data in case of a Crypto-locker attack. We keep it simple and just have a redirect of their Documents and set the access to Exclusive. Only time we ever need to touch these folders is when an user leaves the company and at that time we seize ownership. Only ever set up 'home folders' on one or two small business sites, and found they were very seldom used. However, a few users had figured out that they were an ideal place to store porn or pirate stuff because even the admin couldn't see what was in there.

No comments:
Post a Comment